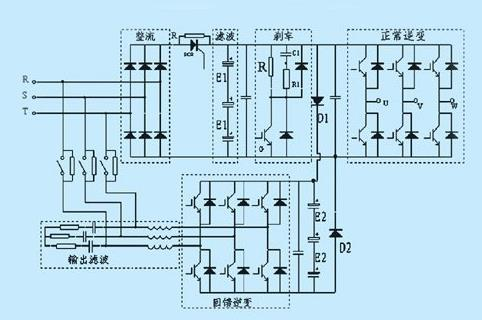
A Variable Frequency Drive (VFD) is a power control device that utilizes variable frequency technology and microelectronics to regulate the operating frequency of an AC motor’s power supply.
A VFD primarily consists of rectifier (AC to DC conversion), filter, inverter (DC to AC conversion), braking unit, drive unit, detection unit, and microprocessor unit.
The VFD adjusts the output voltage and frequency by switching its internal IGBTs, providing the required power supply voltage based on the motor’s actual needs to achieve energy savings and speed regulation. Additionally, VFDs incorporate numerous protective functions, such as overcurrent, overvoltage, and overload protection.
With the continuous advancement of industrial automation, VFDs have gained extensive application. A Variable-Frequency Drive (VFD) is a power control device that utilizes variable-frequency technology and microelectronics to regulate AC motors by altering the frequency of their operating power supply.
The main TOP circuit of a VFD is illustrated below: